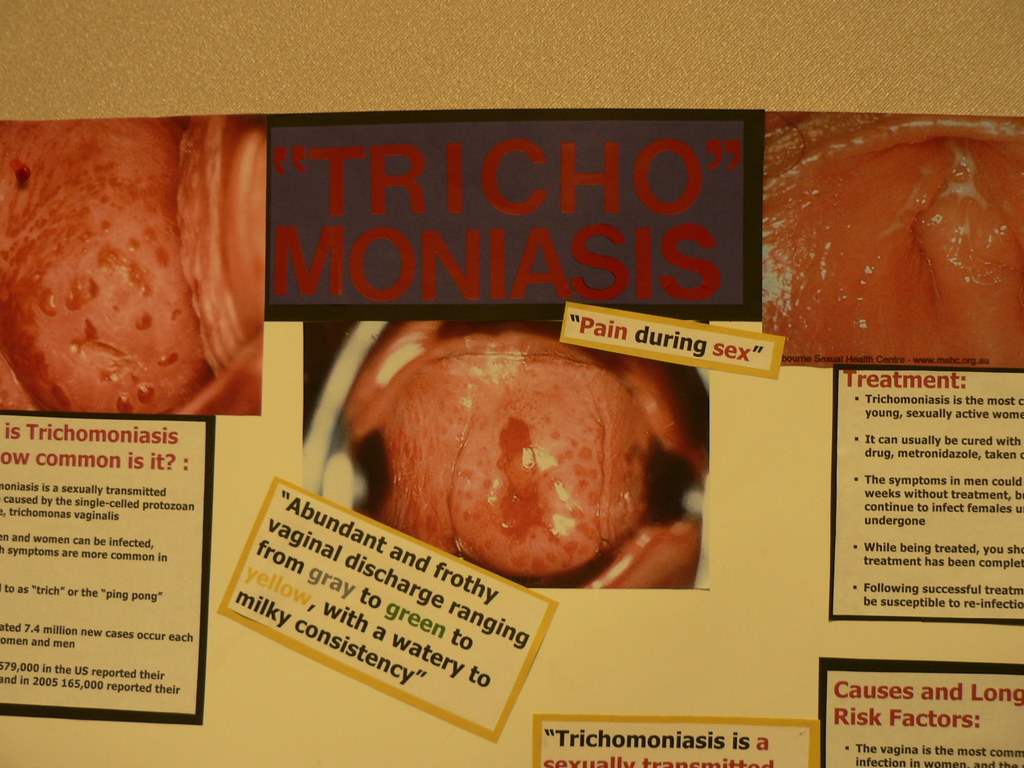
Trichomoniasis is an STD that affects millions of Americans in a year. It is caused by a parasite and can be treated with antibiotics. In fact, there are about 3.7 million cases of trichomoniasis in the United States each year. Trichomoniasis is the most common curable sexually transmitted infection in the United States. The CDC also reports that the rate of trich infection in the United States is about 7% for women and 3% for men.
And since trich is considered to be one of the most common STDs, part of the concern also revolves on the period of “dormancy” of this disease.
So how long can trichomoniasis be dormant in a woman then? If you’re interested to get more information, we encourage you to keep reading as we’ll talk about this topic in this post.
What Is A Period Of Dormancy
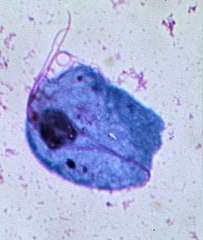
A period of dormancy is a time when an infection is not active. For sexually transmitted infections, this may mean that the infection is not causing any symptoms and is not able to be spread to other people. However, it is important to note that even during a period of dormancy, an infection can still be passed on to others. It is also important to remember that just because an infection is not active, does not mean that it cannot be treated.
In the case of trichomoniasis, there is no true period of dormancy. In fact, trich is a sexually transmitted infection that can be dormant in a woman for years. And in some cases, it may never cause any symptoms and the woman may not know she has it. However, trich can be passed on to sexual partners during this time, which is why it’s important to get tested and treated if you think you may have been exposed.
If there are noticeable symptoms however, a woman who is infected with trich may experience a foul-smelling vaginal discharge, pain during urination, and itching and irritation in the genital area. These symptoms can come and go, and may be worse during menstruation. If you have any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a doctor so you can get treated.
There are three main stages of the infection: primary, secondary, and tertiary.
The primary stage is the initial stage of the infection and is usually the least severe. Symptoms may include discharge from the penis or vagina, itching or burning sensations around the genitals, and pain during sex. In most cases, the symptoms will go away on their own within a few weeks. However, if left untreated, the infection can progress to the secondary stage.
The secondary stage is more serious and can last for several months. Symptoms may include a more significant discharge from the vagina, pain during urination, pain in the lower abdomen, and fever. If left untreated, the infection can progress to the tertiary stage.
The tertiary stage is the most serious and can lead to long-term health problems. Symptoms may include difficulty urinating, pain during sex, infertility, and chronic pelvic pain. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention right away.
What You Need To Do If You’re Infected With Trich
If you think you have trichomoniasis, it is important to seek treatment as soon as possible. Treatment usually lasts for around 7 days, but it is important to follow all of the instructions your doctor gives you in order to make sure that the infection clears up completely. You can also get STD prescriptions from CureDose.com by visiting their website.
There are a few different treatments for trichomoniasis. The most common is antibiotics, which can be either oral or topical. There are also medications that can be prescribed to help relieve the symptoms of trichomoniasis. However, it is also important to note that trichomoniasis can be dormant in a woman for up to eight weeks. This means that even if you are no longer experiencing symptoms, you may still be infected.
Therefore, it is important to get retested for trichomoniasis after you have completed treatment. If you are pregnant, it is especially important to get retested, as trichomoniasis can lead to preterm labor.
The Importance Of Being Tested Again After Treatment
After you have been treated for trichomoniasis, you should get tested again after 3 months to be sure the infection is gone. Some people can still have the infection even after being treated, so it’s important to get tested again to make sure you are cured. Trichomoniasis can stay in your body for a long time and cause problems, so it’s important to get rid of it as soon as possible.